Power Electronic Control Design for Stable Circuit Diagram In the realm of motor control circuit design, the power supply plays a crucial role in ensuring the proper operation and efficiency of the system. The power supply characteristics are essential factors to consider during the design process, as they directly impact the overall performance and reliability of the circuit. Basics of Motors + Motor Control - what are they, and what do we want to do? A motor is an electro-mechanical device that takes electrical energy and converts it to mechanical energy, and vice-versa. Motors are super cool! They spin! And understanding how a motor works is critical for certain systems, especially if you want to design a motor controller. The lecture video itself contains a more
Conclusion Understanding the different types of motor control circuits is crucial for ensuring efficient and reliable operation of electric motors. By selecting the appropriate circuit and implementing proper wiring practices, you can optimize system performance and minimize downtime.

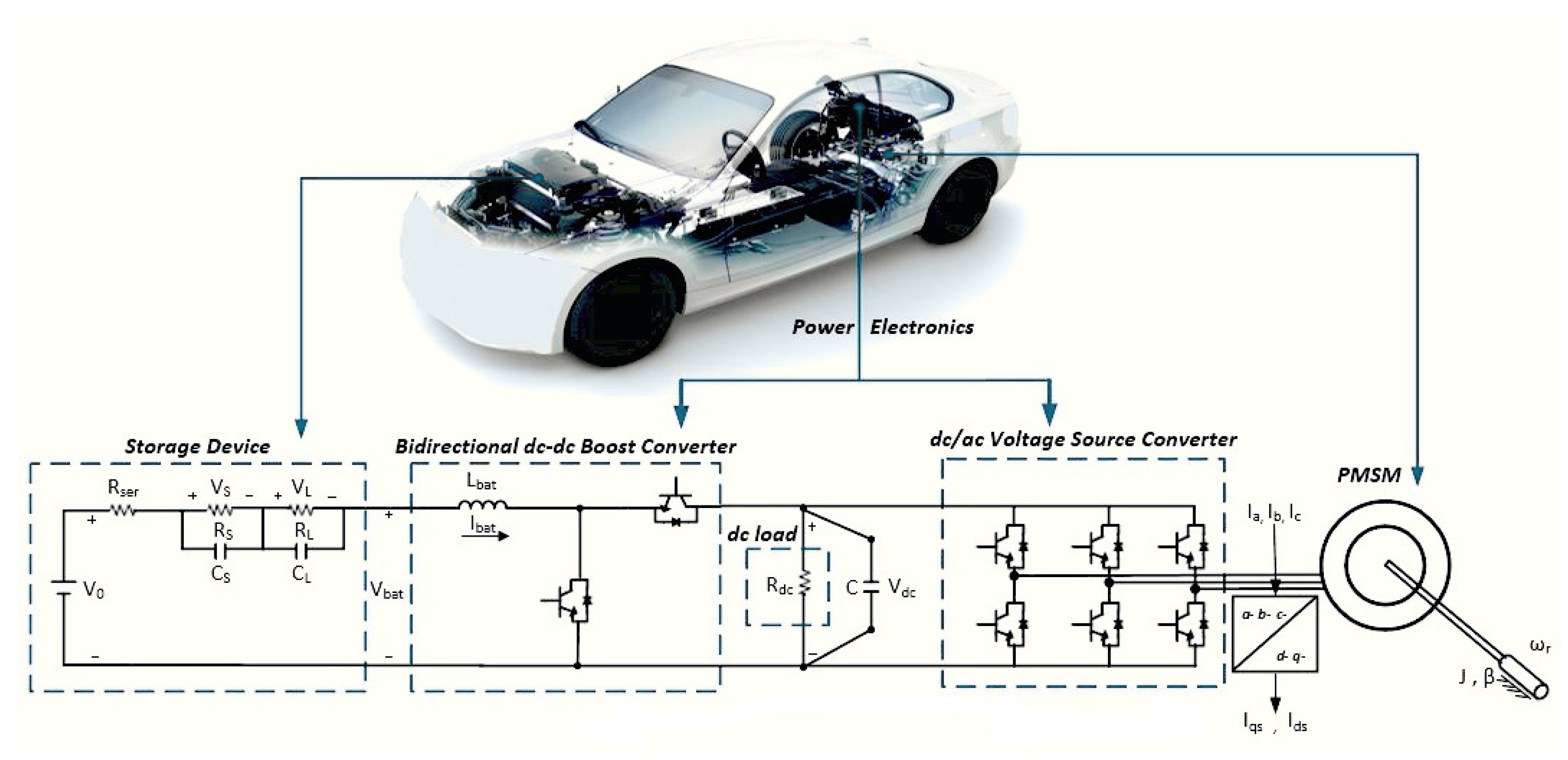
Guide to Basic Electric Motor Control System Design Circuit Diagram
AC induction motors have simple and inexpensive control electronics, making them easy to implement in motor control systems. The use of a feedback device is optional, providing flexibility in design.

Motor control circuit diagram: Learn how to design and implement a motor control circuit with this comprehensive guide. Includes circuit diagrams and step-by-step instructions. Motor control circuits are often connected to lower voltages than the motor they control to make it safer for operators and maintenance personnel. Motor control circuits are electrical systems that allow you to control the speed and direction of motors. These circuits are used in a variety of industrial, medical, and recreational applications, from robotic arms to automated door openers.

10 Essential Electric Motor Control Circuit Diagrams You Need to Know
The next figure below shows a very simple DC motor speed controller circuit that employs a MOSFET as a high-power potentiometer (rheostat). The circuit is designed to work with 12 volt DC motors having a peak current usage of below 5 amp.
